Septic Systems
Septic Systems
Septic systems play an essential role in effectively treating wastewater in areas without municipal sewage treatment. A properly designed, maintained and managed system can provide adequate treatment for most pollutants and is key to minimizing failures and resulting environmental impacts.
Septic system failures release untreated wastewater into the environment. Untreated wastewater contains excessive nutrients (nitrogen and phosphorus) that can harm native plant and fish populations in Kentucky's surface waters. Wastewater's excessive organic matter can choke off the oxygen supply to streams and rivers. Bacteria levels in impacted waters can exceed regulated body contact standards, abruptly halting recreational use of beaches, lakes and streams.
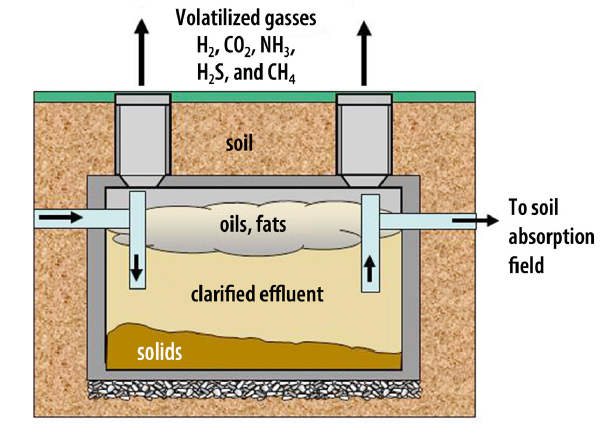
How it works: The primary treatment device is the septic tank. This is a large chamber that collects household sewage. Waste enters the tank through piping from your home. Effluent or liquid waste ((99.99% water) passes through the tank and is dispersed in a soil absorption field. Components that are lighter than water (fats and oils) and soilds that are heavier than water are retained in the tank. Solids are separated through settling. Most of the solid material breaks down into gaseous by-products which are vented through your home's plumbing vent system. The remaining solids that do not biodegrade accumulate in the tank and must be removed every few years.
Maintenance and Care: Install effluent screens on the outlet to screen out any large solids that may plug pores in the soil absorption field. These screens need to be checked every 6-12 months and rinsed, as needed, to minimize clogging. Have your septic tank serviced regularly by a qualified professional to check for cracks or leaks. Solids should be pumped from the septic tank every 3 to 5 years.
Remember! Do not park or drive over your septic tank with anything heavier than a riding lawn mower and use water in your home conservatively.
Links to additional resources:
Septic Tanks: The Primary Treatment Device of Septic Systems
